Tech
How To Use RMF Continuous Monitoring to Keep a Quality Control Plan Current

In the fast-paced digital age of today, cybersecurity threats are ever-changing, and hence it is important for Federal agencies to maintain their defenses up to date. Risk Management Framework (RMF) Continuous Monitoring is a mechanism that allows organizations to monitor their cybersecurity program vigilantly and respond to upcoming threats in a timely and proactive manner. Through continuous monitoring, organizations can detect and remediate threats before they are used to exploit vulnerabilities.
7 Steps of Risk Management Process
The risk management process is a structured method that seeks to manage uncertainty in construction and capital projects. Through proactive identification of potential risks, evaluation of their impact, and planning for the mitigation of the same, project teams can better ensure success. This structure, referred to as the Project Risk Management Process or Risk Management Framework (RMF), ensures that risks are properly controlled throughout the life of the project. Here are the following 7 RMF steps which defines risk management process-
- Establish the Context- Setting the context is the initial and most important step in the process of risk management. It includes defining the scope and purpose of the project, the internal and external environment, and the involved stakeholders.
- Risk Identification- After setting the context, the second step is identifying potential risks that may affect the project. Risk identification is the process of searching systematically for risks from different sources and recording their characteristics.
- Risk Analysis- Identifying risks is followed by analyzing them. Risk analysis in project management analyzes the possible effects and probability of occurrence for each risk, so that a risk rating or risk score can be allocated based on severity. It is here that all risks are assigned a rating or score, which sets the process of prioritization on what to tackle first.
- Risk Evaluation- With the analysis, you can assess the risks. Risk assessment entails comparing your analysis results against established risk criteria in order to ascertain the importance of each risk and choose the proper responses.
- Risk Treatments and Controls- Risks having been assessed, the following step is to construct and implement responses to resolve them. Risk treatments and controls are crucial for handling the risks effectively.
- Monitoring and Review- Monitoring and reviewing risks entail the ongoing process of observing and assessing both internal and external environments in order to ensure risk management activities are still effective, relevant, and congruent with the objectives of the organization.
- Communication and Consultation- Good communication and consultation are important to the success of the risk management process. Informing all stakeholders about risks and consulting them ensures that everyone is in line and that the project proceeds smoothly.
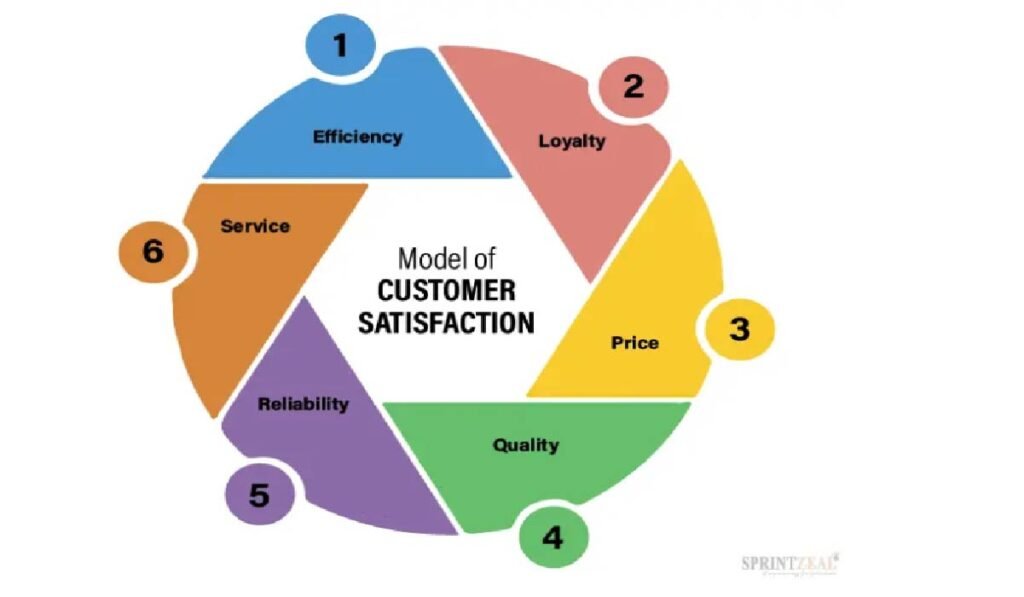
How to Create a Quality Control Plan?
A Quality Control Plan is an organized document that explains how a manufacturing firm ensures its products always meet specified quality standards. It serves as a template for staying consistent, reducing errors, and guaranteeing quality requirements are fulfilled during the life of a process or project.
Why Do You Need a Quality Control Plan?
A Quality Control Plan keeps your process on track. It sets clear standards, outlines who does what, and shows how to catch and fix issues before they become problems. Without it, you’re risking inconsistent results, wasted resources, and unhappy customers. It also keeps your team aligned with no confusion, no guesswork. Everyone knows what “quality” means and how to deliver it. Your QCP becomes a tool for improving efficiency, reducing waste, and making smarter decisions based on real data. If you’re working with clients or under strict regulations, having a solid plan in place shows you’re reliable and in control.
What Is Meant by Continuous Monitoring?
Continuous monitoring refers to the ongoing process of tracking and evaluating the security and privacy status of an information system. It facilitates effective near real-time risk management through automation and state-of-the-art practices for monitoring controls and modifications to the system or environment to enable an Authorizing Official (AO) to decide whether or not to authorize a system to continue operating or use inherited common controls. Continuous monitoring strategy supports continuous authorization with data to inform continuous risk determinations subsequent to the initial system or common control authorization.

What Is Continuous Monitoring in RMF?
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Risk Management Framework (RMF) offers a disciplined method for risk management. Continuous monitoring is one of them. NIST 800-137 defines information security continuous monitoring as an organization’s “continuing awareness of their information security posture, vulnerabilities, and threats,” and tackles the evaluation and analysis of security control efficacy. By adopting ongoing monitoring, organizations are able to continually review and manage security threats, keeping systems secure in the long term. Conventional risk management methods are static and periodic.
Most organizations only review risks once a year or when performing a compliance audit, putting them at risk of vulnerabilities for long periods of time. Continuous monitoring, in contrast, offers real-time visibility and tracking of possible risk and vulnerabilities so that organizations are able to be proactive in managing risks. Continuous monitoring enables organizations to promptly detect and respond to threats, minimizing the effort and time needed to resolve security breaches. Through continuous monitoring of their systems and networks, organizations can ensure that they comply with the required security controls and requirements. This assists them in preventing expensive fines and penalties for non-compliance.
Understanding the RMF Framework and its Contribution to Continuous Monitoring
The RMF framework is an integrated methodology for risk management through which an organization discovers, measures, and controls possibilities of threat and vulnerabilities within its computer infrastructure.
Continuous monitoring is a part of the framework in which there is constant feedback on the efficacy of security controls and allowing organizations to make informed decisions regarding methods of risk management. The RMF framework is based on six steps: categorization, selection, implementation, assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring. Ongoing monitoring covers all six steps, giving feedback on an ongoing basis and making adjustments in security where necessary. One of the most significant advantages of the RMF framework is that it delivers a standardized method of risk management, one that can be used for any organization or industry.
This ensures that all dangers and vulnerabilities are accounted for and addressed in an ongoing and systematic way. In addition, the RMF model puts great emphasis on continuous communication and collaboration among various stakeholders, including business leaders, risk managers, as well as IT professionals, to make sure that risk management approaches are aligned with organizational objectives and goals. Another significant feature of the RMF framework is its emphasis on continuous improvement. This ensures that the organization is always aware of the latest threats and vulnerabilities and can respond swiftly and efficiently to any security breaches that might arise.
Conclusion
In summary, the RMF unifies control, terms, and enhances reciprocity among government agencies. It places risk ahead of one-size-fits-all solutions, incorporates security into systems, and speeds up security response. Ongoing monitoring improves federal agency cybersecurity, allowing for detailed reporting and risk management. Ongoing monitoring in RMF is an essential practice for organizations that aim to reduce potential risks and vulnerabilities in their IT infrastructure. Continuous monitoring involves thorough planning and implementation but offers immense benefits, such as enhanced productivity, enhanced compliance, and enhanced trust in the security posture of the organization.
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Jennifer Rauchet?: All You Need To Know About Pete Hegseth’s Wife
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Mindy Jennings?: All You Need To Know About Ken Jennings Wife
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Enrica Cenzatti?: The Untold Story of Andrea Bocelli’s Ex-Wife
-

 Celebrity2 years ago
Celebrity2 years agoWho Is Klarissa Munz: The Untold Story of Freddie Highmore’s Wife