Health
How Is Endoscopic Surgery Different From Traditional Surgery
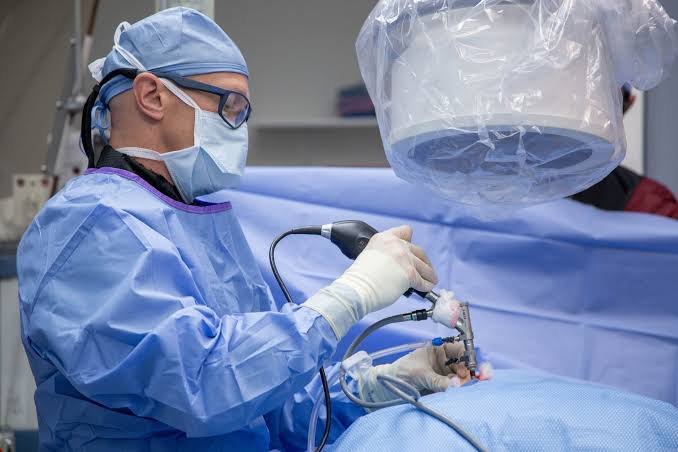
Endoscopic surgery, often referred to as minimally invasive surgery, has revolutionized the field of medicine, providing patients with a more comfortable and efficient alternative to traditional open surgeries. This procedure involves the use of specialized instruments, including an endoscope, to perform surgeries with minimal incisions, often resulting in faster recovery times and less postoperative discomfort. In this article, we will compare endoscopic surgery to traditional surgery, highlighting key differences and discussing the benefits that make endoscopic techniques increasingly popular in modern medical practice.
What Is Endoscopic Surgery?
Endoscopic surgery is a type of minimally invasive surgery that uses an endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera attached, to visualize internal organs and tissues. The endoscope is inserted through small incisions or natural body openings, such as the mouth or anus. The images captured by the camera are transmitted to a monitor, allowing surgeons to guide specialized instruments to perform procedures with great precision.
Unlike traditional surgery, where larger incisions are required to access the target area, endoscopic surgery typically involves smaller cuts, which means less trauma to the body and a quicker recovery for the patient. This technique can be used in a variety of surgical specialties, including gastroenterology, orthopedics, gynecology, and urology.
How Is Endoscopic Surgery Different From Traditional Surgery?
1. Size and Type of Incision
The most obvious difference between endoscopic and traditional surgery is the size of the incisions. In traditional surgery, large incisions are often required to expose the area being operated on. This can result in greater blood loss, a longer hospital stay, and more noticeable scarring. In contrast, endoscopic surgery only requires small incisions, which are often no more than a few millimeters in size. The use of smaller incisions significantly reduces the trauma to the surrounding tissues.
For example, in traditional gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy), the surgeon must make a large incision in the abdomen to access the organ. However, in endoscopic surgery, only small incisions are made, through which the endoscope and surgical tools are inserted. This method is not only less invasive but also results in less postoperative pain and scarring.
2. Recovery Time
One of the major benefits of endoscopic surgery over traditional surgery is the significantly shorter recovery time. Because the procedure is less invasive and involves smaller incisions, patients often experience less pain and discomfort after surgery. This leads to a faster return to daily activities and work. In many cases, patients can even go home the same day as the surgery.
Traditional surgery, on the other hand, typically requires longer recovery periods due to the larger incisions and greater trauma to the body. Depending on the procedure, patients may need to stay in the hospital for several days and take weeks to fully recover.
3. Risk of Infection
With traditional surgery, the risk of infection is generally higher due to the larger incisions and longer exposure of internal organs. The healing process can also be slower, leaving the wound more susceptible to infection. However, in endoscopic surgery, because the incisions are smaller, there is less risk of infection. Additionally, the use of specialized sterile instruments and the camera system helps minimize contamination during the procedure.
4. Precision and Visibility
Endoscopic surgery offers superior precision compared to traditional methods. The endoscope’s camera provides high-definition, real-time images of the surgical area, allowing surgeons to navigate with greater accuracy. This enhanced visibility is especially beneficial in delicate surgeries, such as those involving the brain, spine, or internal organs, where precision is crucial.
In traditional surgery, while surgeons may use direct visualization or imaging techniques such as X-rays, they do not have the same level of detailed, real-time visuals that an endoscope provides.
5. Cosmetic Outcomes
The cosmetic outcome of surgery is often a consideration for many patients, especially when it comes to procedures that leave visible scars. Because endoscopic surgery involves smaller incisions, the resulting scars are significantly smaller and less noticeable compared to traditional surgery. This is a particularly important factor for patients undergoing procedures in visible areas, such as the face or abdomen.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial costs of endoscopic equipment may be higher, the overall cost of endoscopic surgery can be lower than traditional surgery. The reduced hospital stay, shorter recovery time, and lower complication rates associated with endoscopic procedures can result in fewer hospital visits, less time off work, and ultimately a more cost-effective treatment for the patient.
In traditional surgery, the longer recovery period and potential for complications often lead to higher overall costs.
What Are the Applications of Endoscopic Surgery?
Endoscopic surgery has a wide range of applications across various medical specialties. Some common procedures that can be performed using endoscopic techniques include:
- Gastrointestinal Procedures: For conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), colorectal cancer, or Crohn’s disease, endoscopic surgery can be used for diagnosis and treatment, including biopsies, removal of polyps, and bowel resections.
- Gynecological Surgeries: Laparoscopic surgery, a type of endoscopic surgery, is frequently used in gynecology for procedures such as hysterectomies, fibroid removal, and ovarian cyst removal.
- Orthopedic Surgeries: Endoscopy can be used to treat joint problems, such as repairing torn ligaments or cartilage in the knee, shoulder, or hip.
- Urological Surgeries: Endoscopic surgery is commonly used in the treatment of kidney stones, prostate issues, and bladder conditions.
- Cosmetic Procedures: Many cosmetic surgeries, such as facelifts or tummy tucks, can be performed endoscopically, reducing scarring and recovery time.
Conclusion
Endoscopic surgery represents a significant advancement in the medical field, offering numerous benefits over traditional surgery. From smaller incisions to shorter recovery times and reduced risk of infection, endoscopic procedures provide patients with a less invasive, more efficient treatment option. While not every surgery can be performed using an endoscope, its growing range of applications makes it a crucial tool in modern medicine.
Whether for routine diagnostic procedures or complex surgeries, endoscopic surgery is transforming how medical professionals approach treatment, providing patients with faster, safer, and more comfortable outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, the potential applications of endoscopic surgery will likely expand, offering even more effective solutions for a wide array of health issues.
In addition to the medical benefits, patients may also appreciate the cosmetic advantages, such as smaller, less noticeable scars. Just as a cotton natural dress offers comfort and style for everyday wear, endoscopic surgery provides a comfortable and efficient solution for a wide variety of health concerns, making it an increasingly popular choice for patients worldwide.
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Jennifer Rauchet?: All You Need To Know About Pete Hegseth’s Wife
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Mindy Jennings?: All You Need To Know About Ken Jennings Wife
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Enrica Cenzatti?: The Untold Story of Andrea Bocelli’s Ex-Wife
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Klarissa Munz: The Untold Story of Freddie Highmore’s Wife